Contents
Approved by John Heim
Revised 6/20
6.1 Policy
6.2 Scope
6.3 Applicability
6.4 Exceptions
6.5 Work Planning and Control Process Overview
6.6 Roles and Responsibilities
6.7 Definitions
6.8 Required Work Processes
- Work Process A. Activity Manager: Overview
- Work Process B. Activity Manager: Division Settings, News, and Targeted Communication
- Work Process C. Activity Manager: Manage Project
- Work Process D. Activity Manager: Create Activity
- Work Process E. Activity Manager: Release Activity for Review and Approval
- Work Process F. Activity Manager: Assign and Authorize Worker
- Work Process G. Activity Manager: Review Activity and Accept Work Conditions
- Work Process H. Activity Manager: Cancel Activity
- Work Process I. Activity Manager: Close Activity
- Work Process J. Activity Manager: Edit Activity
- Work Process K. Activity Manager: Renew Activity
- Work Process L. Activity Manager: Delegate Role
- Work Process M. Delivery Options for Safety-Related Training
- Work Process N. Activity Manager: Assigning Opt-Out Status
6.9 Source Requirements
6.10 Reference Documents
6.11 Appendices
- Appendix A. Work Planning and Control Equivalence Worksheet
- Appendix B. Facility-Based Authorizations
- Appendix C. Hazard-Specific Information Requirements
Note:
🚩🚩 Denotes a new section
🚩 Denotes the beginning of changed text within a section
🛑 Denotes the end of changed text within a section
____________________
6.1 Policy
At Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), all work must be authorized before it is performed. Work authorization has two distinct components. The work itself must be planned, reviewed, and authorized before it may proceed. Individual workers must then be properly trained and authorized before they can proceed with their assigned work activities. This dual-step authorization process helps ensure work is performed safely by authorized staff.
Berkeley Lab uses formal work planning and control (WPC) processes such as Activity Manager, radiological work authorizations, construction job hazards analysis, subcontractor job hazards analysis, and in some cases facility-based authorizations to:
- Define the scope of work that will be performed
- Identify the hazards associated with this work
- Identify the controls necessary for the hazards
- Authorize work
- Assign and authorize workers to perform work activities
These formal WPC processes are the means by which line management reviews and authorizes work and authorizes workers to perform work. Work may not proceed until authorized by management, and workers may not perform work until they are assigned to one or more work activities and have been authorized by line management. This includes unpredictable, short-term, or unusual work, all of which must be reviewed and authorized.
Work is authorized following a risk-based approach. Work involving low or moderate hazards is authorized by line management. Work involving higher hazards requires concurrence of the Environment/Health/Safety (EHS) Division in addition to line management authorization and supervisor approval.
Workers are authorized at a level commensurate with their knowledge and skill level given the particular hazards associated with work. Workers may be authorized to work; authorized to work under direct supervision; or not authorized to work. The worker authorization level is determined by line management.
Work is reviewed and the authorization renewed periodically based on the hazards associated with the work or when the work, hazards or controls change significantly. Worker authorization must be renewed on the same schedule.
Equivalent work authorization systems are allowed, but these must be approved by the EHS Division Director.
6.2 Scope
Safety of all operations at Berkeley Lab is managed according to the principles outlined in PUB-3140, Integrated Environment, Safety & Health Management Plan: Integrated Safety Management (ISM) System. The following five functions form the core of the ISM process:
- Defining Work: The tasks to be performed for any activity must be clearly defined.
- Analyzing Hazards and Risks: Once the tasks have been defined, the hazards and risks associated with the activity — in particular, the risks to employees, the public, and the environment — must be determined.
- Establishing Controls: Controls (e.g., engineering, administrative, personal protective equipment) sufficient to reduce the identified risks must be implemented.
- Performing Work: Any time that work is performed, established controls must be used.
- Feedback and Improvement: The activity and its associated controls must be continually examined to determine if the controls are effective; if not, changes must be made. If additional safety can be achieved, the changes necessary to do so must be made.
These five core functions apply at all Berkeley Lab operational levels: institution, division or department, and individual projects or work activities. For a description of how these core Environment, Safety & Health (ES&H) functions are applied at each level, and of the various programs and policies in place to ensure that they are applied, see PUB-3140, Integrated Environment, Safety, & Health Management Plan: Integrated Safety Management (ISM) System.
Work Planning and Control is a key principle of Berkeley Lab’s safety policy. It is a review and management approval process designed to ensure that procedures, controls, and required resources are in place before work begins, and that workers are authorized by line management to perform work. All work at Berkeley Lab proceeds under work authorizations according to the following processes:
- Line Management: An authorization that is in place by explicit documentation and administered by the division responsible for the work. Examples include Activity Manager or equivalent processes (e.g., Advanced Light Source’s Experiment Safety Sheet for users; see Appendix A, Work Planning and Control Equivalence Worksheet). Work involving hazards such as high stored energy, toxic gas, live electrical exposure or unsealed radioactive materials is subject to subject matter expert (SME) review and concurrence with the scope of work, required procedures and controls, authorized materials, and equipment to be used prior to line management approval. Work with some hazards requires supplemental authorizations, such as Radiological Work Authorizations and authorizations for research involving human or animal subjects.
- For non-construction subcontractors, the Subcontractor Job Hazards Analysis (sJHA) program is used to ensure that all non-construction subcontractor work is performed safely and in accordance with Berkeley Lab requirements.
- For construction activities, the requirements of Chapter 10 Construction Safety are followed to ensure that construction subcontractors adequately evaluate hazards and implement safety controls.
- Facility-Based: Hazard analysis and controls based on the facility as a whole rather than on individual operations. Examples include Safety Analysis Documents, air and water discharge permits, some other regulatory permits, and National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) / California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA) analyses. See Appendix B, Facility-Based Authorizations, for details.
6.3 Applicability
This program applies to all staff, affiliates, and others who perform work at Berkeley Lab.
6.4 Exceptions
Those performing only work commonly performed by the public, who work exclusively under a separate work authorization system such as the Subcontractor Job Hazards Analysis process or Construction Health and Safety process, who work only at a site not managed by Berkeley Lab and have existing work authorization processes, or who work only on the UC Berkeley Campus. Note that Berkeley Lab work planning and control covers Berkeley Lab personnel working at off-site locations that do not have existing authorization processes.
6.5 Work Planning and Control Process Overview
Work Planning and Control (WPC) is performed at the activity level. Divisions begin the WPC process by authorizing Project Leads to oversee work. Project Leads organize work into projects and activities and assign Activity Leads. Activity Leads develop activities by defining work, identifying hazards associated with the work, and implementing controls. The Activity Lead is also responsible for assigning and authorizing workers to perform work. Activity Leads may delegate this responsibility to Activity Lead Designees who are able to assign and authorize workers on specific activities.
The Project Lead may serve as the Activity Lead and/or assign the role to one or more Activity Leads. Neither the Project Lead nor the Activity Lead needs to be a member of the authorizing division. The Project Lead maintains overall control and responsibility for each activity within their project.
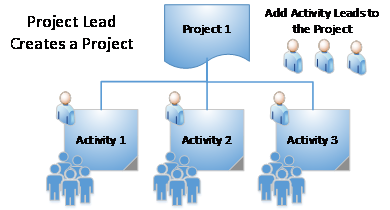
Figure 1. Activity-Based Work Planning
The primary system for work planning is Activity Manager. Activity Leads use Activity Manager to define the work, identify hazards, and develop controls. Hazards are assigned one of three risk levels: 1 – low hazard; 2 – moderate hazard; or 3 – high hazard, predetermined by the EHS Division through the Integrated Hazard Analysis (IHA) system. The highest hazard associated with the activity determines the activity’s overall risk level. The activity’s overall risk level determines the level of EHS participation, division line-management approval, and worker’s supervisor approval.
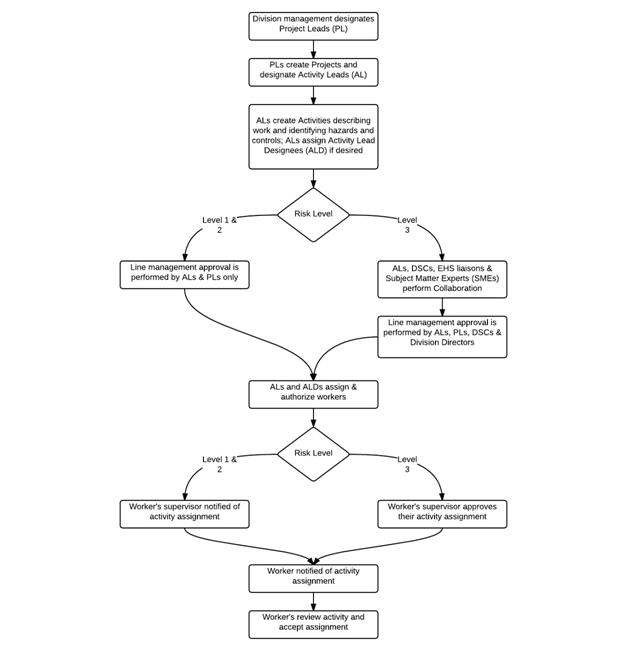
Figure 2. Work Planning and Control Process Overview. (Click here to download a printable PDF of Figure 2.)
Activity Manager automatically assigns division-specific sequential project and activity numbers. NOTE: Activity Manager project and activity numbers do not correlate to the Lab’s Financial Management System project and activity identifiers.
6.6 Roles and Responsibilities
| Role | Responsibilities |
| Division Directors |
|
| Workers (Employees, Visitors, and Affiliates) |
|
| Principal Investigators, Managers, HR Supervisors, and HR Work Leads |
|
| Project Lead | The Project Lead is the person with overall responsibility for the safety for a defined set of activities. Project Leads:
The Project Lead may serve as the Activity Lead and/or assign the role to one or more Activity Leads. Though an assigned Activity Lead can prepare the documentation for a new activity, no new activity can be undertaken without the final approval of the Project Lead. The Project Lead may be the direct HR line supervisor or any other staff member assigned by division management to the position of Project Lead. This position is not the equivalent of an HR Supervisor position. Note: For work involving a Risk Level 3 radiological hazard requiring a Radiological Work Authorization (RWA) or X-Ray Authorization (XA), the Project Lead role is equivalent to the RWA or XA Principal Investigator (PI) role. |
| Activity Lead | An Activity Lead is anyone who directs, trains, or oversees the work and activities of one or more workers. Activity Leads provide instruction on working safely and the precautions necessary to use equipment and facilities safely and effectively. Activity Leads:
The Activity Lead may be a direct HR line supervisor or any other staff member assigned by the Project Lead to the position of Activity Lead. This position is not the equivalent of a HR Supervisor position. (Note: Certain representative workers may be barred from acting as Activity Leads because of contract restrictions. Restrictions will be communicated by EHS using appropriate forums.) Note: For work involving a Risk Level 3 radiological hazard requiring an RWA or XA, the Activity Lead role is equivalent to the RWA or XA PI-designee role or the PI role. |
| Activity Lead Designee | As assigned by the Activity Lead, the Activity Lead Designee:
|
| Facilities Division |
|
| EHS Liaisons |
|
| EHS Division Director |
|
6.7 Definitions
| Term | Definition |
| Activity Manager Work Authorization | Activity Manager work authorization requires line management to describe the scope of work for each activity, determine the hazards of that work, and review and refine the controls prescribed for those hazards. The documentation of that analysis and the assigned tasks, once fully approved by line management, serves as work authorization for the individual assigned to perform the work. The work authorization document is maintained as an electronic record in the Activity Manager database. |
| Activity | A task involving one or more steps needing to be accomplished by one or more individuals to achieve a goal. |
| Activity that is commonly performed by the general public | An activity that people in the general public perform with hazards and environmental impacts accepted by those performing the activity and controls that require little or no guidance or training in order to perform the work safely while minimizing environmental impacts. |
| CHESS | Comprehensive Health, Environmental and Safety System |
| DOW | Description of Work |
| DSC | Division Safety Coordinator |
| Exposure assessment | The process of defining exposure profiles and judging the acceptability of workplace exposures to environmental agents. These assessments may be quantitative, semi-quantitative, or qualitative. These assessments are generally conducted by an Environment/Health/Safety (EHS) professional, which may include industrial hygienists or safety engineers. These assessments may be conducted for representative employees and are not required for each individual. In all cases, employees have full access to exposure-monitoring information, including situations where an individual’s exposure is not monitored. |
| Facility-based authorization | Hazards analyses and controls are based on the facility as a whole rather than on an individual operation. Examples include safety-analysis documents, air and water discharge permits, and NEPA/CEQA analyses. |
| Hazard | The potential to cause harm. Hazards are associated with tasks; if hazards are not controlled, they can cause illness or injury. |
| Hazard assessment | A preliminary evaluation (or screening) of an activity to determine if a more comprehensive exposure assessment is required. Hazard assessments can be performed by work leads, supervisors, workers or an EHS professional. Hazard Assessments are one form of Baseline Exposure Assessment. |
| OJT | on-the-job training |
| Opt-Out Status | The status of an employee or affiliate who is not performing Work, and thus is not to be assigned to an Activity. The opt-out status is specifically assigned by the Supervisor, based on the Supervisor’s determination that the person will not be performing any Work |
| Project | A planned work with specific purpose consisting of one or more activities. |
| RWA | Radiological Work Authorization |
| SJHA | Subcontractor Job Hazards Analysis is a set of documents that establishes that a subcontractor has adequately identified the hazards of work and defined appropriate controls for those hazards. The SJHA is required for authorization of subcontractor work. |
| Task | A discrete element of work. |
| Work | An activity or set of activities that can be analyzed using Activity Manager. |
| XA | X-Ray Authorization |
6.8 Required Work Processes
Work Process A. Activity Manager: Overview
Work Process B. Activity Manager: Division Settings, News, and Targeted Communication
Work Process C. Activity Manager: Manage Project
Work Process D. Activity Manager: Create Activity
Work Process E. Activity Manager: Release Activity for Review and Approval
Work Process F. Activity Manager: Assign and Authorize Worker
Work Process G. Activity Manager: Review Activity and Accept Work Conditions
Work Process H. Activity Manager: Cancel Activity
Work Process I. Activity Manager: Close Activity
Work Process J. Activity Manager: Edit Activity
Work Process K. Activity Manager: Renew Activity
Work Process L. Activity Manager: Delegate Role
Work Process M. Delivery Options for Safety-Related Training
Work Process N. Activity Manager: Assigning Opt-Out Status
Work Process A. Activity Manager: Overview
Activity Manager Home Page. The Activity Manager system is accessible to all employees and affiliates with a current LDAP login. Activity Manager menu options are available depending on the user’s role in the system:
- Home — The home page is available to all system users. Home consists of a menu bar, My Work, and My Activities. My Work contains informational and actionable messages related to the worker’s activities and roles in the WPC process. My Activities lists all the activities to which the user is assigned and/or serves as the Activity Lead.
- Hazards & Controls — a research tool available to all system users. Review hazard details, or add hazards to the basket and click Continue for a list of required and recommended controls. Note: When using the research hazards function, the controls do not appear in the order of precedence described in Work Process D, Activity Manager: Create Activity.
- My Projects — available to Project Leads. My Projects provides a list of all current projects and associated Activity Leads.
- My Workers — available to supervisors. My Workers provides a list of all of a supervisor’s direct reports, and a list of each worker’s activities and activity-required training.
- Dashboards — provides a selection of available role-based dashboards.
- Activity Search — opens the Activity Manager search tool.
- WPC Settings — available to the Division Safety Coordinator (DSC). DSCs use the WPC Settings page to update Project Lead information and other division-specific settings, compose divisional news, and send targeted communications.
- Support — available to all system users. Support provides a link to the askUs help service.
- Resources — links to a variety of training videos and other helpful resources.
Work Process B. Activity Manager: Division Settings, News, and Targeted Communication
Division Safety Coordinators (DSCs) maintain division-specific work planning and control parameters, compose division WPC news, and send targeted communication from Division Settings page.
- Access Division for Update and News Composition
- DSCs access the Division Settings page from WPC SETTINGS in the main menu.
- If the DSC supports a single division, that division’s settings automatically appear on the Division Settings page.
- If the DSC supports more than one division, the DSC selects the division to be added from the Select Division pull down.
- Risk Level 2 Activity DSC Approval Setting
- Divisions have the option to require DSC approval of all Risk Level 2 activities.
- The DSC sets or removes this requirement by selecting the Yes or No radio button under Activity Risk Level 2 Requires DSC Approval and click the SAVE button.
- Assign Division Director
- In the WPC process, division directors approve Risk Level 3 activities.
- Divisions may assign the division director WPC role to another person by searching for and selecting the replacement, then clicking Change Division Director and click the SAVE button.
- Assign Project Lead
- Divisions must identify who in their division will serve as a Project Lead, thereby authorizing Project Leads to create projects and delegate authority to Activity Leads.
- The Division Director is the Project Lead’s default line management approver for Risk Level 3 activities.
- Divisions may assign an alternate approver per Project Lead. To change a Project Lead’s line management approver, click the edit icon (the pencil), enter the new line management approver’s name, and click Change Line Management Approver, and click the SAVE button.
- Follow the same steps to replace an existing Project Lead. First click the pencil icon, enter the Replacement Project Lead’s name, click Change Line Management Approver, and click the SAVE button..
- When a DSC changes a Project Lead, the new Project Lead replaces the previous Project Lead on all open Projects and active Activities.
- Compose News. Division Safety Coordinators may compose and post divisional WPC-related news in Activity Manager.
- To compose a division-specific news item, select Compose News from the WPC SETTINGS menu.
- Enter the news header, news body, expiration date and applicable hyperlinks. Division-specific news appears on the Activity Manager home page.
- Targeted Communication. Division Safety Coordinators may send targeted communications to Activity Leads and workers.
- To send a targeted communication, select Targeted Communication from the WPC SETTINGS menu.
- Next use the query tool to select the applicable activities (e.g., division activities involving a particular hazard and/or performed in a particular location).
- Compose the message and select whether the message is intended for just the Activity Lead(s) or Activity Lead(s) and workers.
- Click Send Message and the recipients receive a My Work notification containing the message.
Work Process C. Activity Manager: Manage Project
Project Leads begin the work planning and control process by organizing work into projects and assigning Activity Leads.
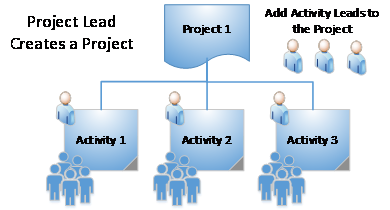
Activity-Based Work Planning and Control
- Create a Project
- A Project Lead may create a project from their Activity Manager home page or from their MY PROJECTS page.
- The Project Lead enters the project name, brief description and Activity Lead(s) (add by clicking + Add Activity Lead) and click the SAVE button..
- MY PROJECTS and EDIT PROJECT
- The MY PROJECTS page provides Project Leads with a summary of all their projects and activities. This page organizes activities by project and provides the status of each activity, (developing, reviewing, collaboration, or active).
- From the MY PROJECTS page, the Project Lead can View Project information and CREATE a PROJECT.
- The View Project selection opens the PROJECT SUMMARY page. The PROJECT SUMMARY displays all project information, Activity Leads, associated activities and their status.
- Select Edit Project to revise project information, add or delete Activity Leads.
- Close a Project
- A Project Lead or DSC may close a project that contains canceled and/or closed activities.
- Select the Project for closure from the MY PROJECTS page.
- Select Close Project from the Choose an Action button.
- Confirm the project closure and click the SAVE button.
- Projects with activities in the Developing, Collaboration, Closed Collaboration, and Reviewing or Active status may not be closed.
NOTE: Activity Manager projects and activity numbers do not correlate to Berkeley Lab’s Financial Management System project and activity identifiers.
Work Process D. Activity Manager: Create Activity
- Initiate Create Activity Process. Activity Leads apply the ISM process for each activity under their management, including: preparing a statement of work outlining the scope of the activity; determining the hazards associated with the work; and designating the controls needed to mitigate the hazards.
- The Activity Lead creates a new project by selecting CREATE ACTIVITY from the Activity Manager Home page, and entering the name of a new activity or searching for an existing activity to copy.
- Activities in any status are available to copy. Copying an activity creates a new activity in the Developing status with the following information available for editing:
- Activity Description
- Description of Work
- Locations
- Hazards (including the hazard itemization and any activity specific information)
- Controls (including any activity specific information)
- Attachments
Worker information is not copied from an existing activity.
- Description
- Enter Activity Name.
- Select the applicable Parent Project.
- The Parent Project Division auto-fills based on the Parent Project selected.
- Select Activity Lead.
- The Activity Lead Division auto-fills based on Activity Lead selected.
- Enter planned Activity Start Date.
- Enter Brief Description (this is not the complete statement of work).
- Enter Activity Lead Designees (ALD) if desired for the Activity.
- Type in name and click Add Activity Lead Designee.
- ALD authority to authorize workers defaults to all workers on the activity. If desired, use Edit Info icon (pencil icon) to adjust the ALD’s authorization privileges. ALDs can authorize all workers on an activity (“All Workers”), or this can be limited to workers added by the ALD to the activity (“Designee Worker Only”).
- Enter Locations where work will be performed.
- Location — Building and room combination (both required) for main site and all leased locations, e.g., the Joint Genome Institute (JGI), the Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI), Potter Street, etc.
- Various — If the Activity is a sitewide function such as Facilities maintenance, select “Various” and enter the location description.
- Infrastructure — e.g., roadways, rooftops, sewer system, etc.
- Off-site — work locations other than those described above, e.g., private businesses and field work.
- Click Add Location for each entry.
- Divisions may use Activity Manager to provide detailed off-site work information such as location details, off-site participants, and emergency response from the information, or “i” icon next to the identified off-site work location.
- Click the SAVE or CONTINUE button.
- Description of Work. Defining work is the first step in the ISM process. The Description of Work (DOW) provides the worker with a clear description of the tasks they will be performing while working under this activity authorization. The detail required in the statement of work depends upon the risk level of the hazards associated with the work.
- The DOW may start with a brief description of the purpose and will include the breadth of the work involved in the activity. For low-risk activities, this can be a broad, general description.
- For moderate to high-risk activities, the DOW should include greater detail. The more detailed description of moderate to high-risk activities should address:
- Materials
- Describe the materials, and how they will be used and handled.
- Give specific controls for hazards that the Activity Lead deems warrant special attention.
- Describe the state of biological materials (fixed, fresh, cultures) and radiological materials (dispersible, fixed, sealed sources) associated with the activity’s significant tasks.
- Processes
- Describe tasks or processes that require specific instructions to be carried out correctly or safely.
- Identify specific steps in procedures that pose a significant safety hazard with details on how to mitigate these hazards.
- Consider attaching and referencing standard operating procedures (SOP), protocols, or instructional videos if tasks require extensive, detailed instruction.
- Provide specific procedures for waste processing or disposal that go beyond waste-handling controls described in the controls.
- Equipment
- Use of equipment that may present hazards to the workers or the environment should be addressed in the Activity. This may include, but is not limited to, furnaces/ovens, autoclaves, robotic equipment, and centrifuges, and/or equipment containing hazardous materials such as gloveboxes containing water- or air-reactive chemicals. Where such hazardous equipment is shared, the Activity must note the responsible individual or group and their contact information.
- Describe the equipment used in the Activity.
- Describe the hazards of the equipment, and the controls for those equipment hazards.
- Provide operating instruction for equipment not covered by OJT or other Activities.
- Materials
- The DOW should include hazard-specific information needed to satisfy review by additional groups such as the Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC). This will only be applicable in select cases. For specifics, refer to Appendix C of this program.
- For work performed in spaces shared with other workers, coordinate the work being performed with the other workers to ensure that any hazards posed by the work are adequately communicated, and that other work is coordinated as appropriate to mitigate exposures to the hazards. This may include, but is not limited to, shared technical areas, shared lab benches, shared fume hoods or glove boxes, etc.
- The DOW should include activity limits or work boundaries, if appropriate. The Activity Lead may also describe restricted tasks that should be considered for higher hazard work where exceeding the safety envelope of the associated controls could have serious consequences.
- Hazards and controls do not need to be addressed within the Statement of Work summary, as they will appear in the Hazards and Controls sections. However, if the Activity Lead feels that specific hazards or controls should be called out, they should be mentioned in this statement. Emergency procedures should be included in the Controls section of the activity.
- The Activity Lead may attach relevant documents and/or links to other information sources from the Attachments page or Worker Detail page. These may include standard operating procedures, protocols, detailed OJT information and checklists, exposure assessment reports, or links to how-to videos.
- The Activity Lead can invite others (e.g., workers, colleagues, subject matter experts) to contribute to the WPC process and review the hazards analysis while under development.
- To add a contributor, click on the Collaboration tab of the Define Work page, enter the contributor’s name, and click Add Contributor and click the SAVE or Continue button.
- Contributors receive a My Work action notice requesting their participation.
- Contributors can edit the scope of work, add attachments, and view hazards and controls.
- Risk Level 3 activities require EHS collaboration, which is automatically established when the Activity Lead releases a Risk Level 3 activity for EHS review. Refer to Work Process E, Activity Manager: Release Activity for Review and Approval.
- Select Hazards. Activities have associated hazards, and the hazards must be identified and evaluated in order to properly prescribe controls. The Integrated Hazard Analysis (IHA) system, accessible via Activity Manager, aids the Activity Lead in the process of identifying hazards and establishing controls to mitigate those hazards.
- Hazards are assigned one of three risk levels:
- Level 1 — Hazards are straightforward; controls are well documented; and failure to utilize controls may result in (worst case) a non-serious and non-debilitating injury (e.g., significant keyboarding, common laboratory chemicals without special hazards used in fume hoods, machine tools, climbing of stepladders, routine facilities maintenance).
- Level 2 — Hazards with a higher inherent risk (e.g., common corrosives or solvents; non-critical lift crane operations; forklift driving). Controls are less straightforward or more situational. Hazards at this level are elevated above those in Level 1 but do not rise to mandatory Subject Matter Expert (SME) review and concurrence.
- Level 3 — Hazards with the highest inherent risk (e.g., high stored energy, toxic gas, live electrical exposure, Biological Use Registration & Authorization). Controls are subject to Liaison and SME concurrence.
- To aid the Activity Lead in selecting hazards, Activity Manager first displays broad hazard categories and guides the user through a series of refinements to select the applicable hazard. Hazards can also be located using the Search Hazard function. The Activity Lead adds applicable hazards to the Hazard Basket. As hazards are added, Activity Manager updates the Activity Risk Level to reflect the highest hazards present on the activity.
- Every hazard includes a risk level, detailed description, links to applicable policy, and may include links to lessons-learned and other references.
- If an activity’s hazard is unavailable from the select hazards menu, contact the Division Safety Coordinator, division EHS liaison, or Health & Safety representative for assistance.
- Hazards are assigned one of three risk levels:
- Review Hazards. Next, the Activity Lead reviews hazards selected, provides additional customized details, as appropriate, and verifies the locations in which activity hazards are present.
- Activity Manager assigns all hazards selected to all locations identified in the Activity Description. If all hazards are present in all locations, then no changes are necessary. The Activity Lead deselects hazards from locations where they do not exist for that activity. Each selected location must have at least one associated hazard. This step is essential for accurate communication of co-located hazards.
- The Activity Lead may provide additional information about the hazard in the Activity-Specific Information column. Additional information may include items such as chemical names and use limits.
- Selecting one or more Risk Level 3 hazards triggers hazard-specific requests for additional information, e.g., specific chemical, concentration, concentration, etc.
- Activities with Risk Level 3 hazards are routed to the appropriate EHS liaison and SME(s) for review, assistance, and concurrence with the hazards analysis.
- Review Controls. Activity Manager presents controls based on the hazards selected. Controls are either required or recommended:
- Required controls — controls that are required by regulation and/or policy, and cannot be waived by the Activity Lead. They may include training, specific administrative and engineering controls, on-the-job training, safety surveys, and procedure documentation.
- Recommended controls — controls that are generally appropriate for the hazard at that risk level, but are not driven by a regulation or policy. The Activity Lead has discretion to determine if the control is appropriate for the given situation and selects/deselects them by turning them “on” or “off.” EHS may use the Recommended Control option to offer choices among related controls, e.g., fume hood, snorkeled work area, or glovebox. Recommended controls that remain on (i.e., are not toggled to “off” during the developing stage) become required controls for the activity.
- Controls initially appear in default order by type:
- Engineering
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Work Practices
- Administrative
- Emergency Response
- Hazard Communication (HazCom)
- Storage/Disposal
- Training
- Medical Surveillance
- Hazard icons appear for each control to help identify what/which hazard(s) triggered the control.
- The Activity Lead may customize required and recommended controls for enhanced specificity. This may include more detail on engineering and administrative controls; modification of controls to fit specific protocols, materials, equipment, or space; specificity as to which tasks a control applies; and the addition of controls not suggested by the hazards selection process. Some controls are intentionally generic, allowing for their application across hazards and in order to minimize redundancy, e.g., “wear chemically resistant gloves.” In these instances the Activity Lead should provide activity-specific details, such as the specific gloves to be work for specific tasks.
- The Activity Lead can re-order controls by clicking and dragging the horizontal bars icon and dropping them into the desired order. EHS may also suggest re-ordering controls for Risk Level 3 activities. The revised order is set upon release for line management approval.
- NOTE: Controls can be reordered by selecting the sort by (chevron) icon next to control Class, Control Name, or Recommended/Required. This reorders the control based on the selected column header. There is no way to revert to the original control class default order.
- Activity Manager interfaces with other Berkeley Lab systems to provide information controls linked to other Berkeley Lab systems.
- Training — Activity Manager and Berkeley Lab Training to provide two-way communication of activity-required training and workers’ training completion status.
- Exposure Assessment — Activity Manager routes Exposure Assessment Survey requirements to the Comprehensive Health, Environmental and Safety System (CHESS). This is triggered when a Risk Level 3 activity is released for EHS review and when the activity is released for line management approval for Risk Level 1 and 2 activities. CHESS does not automatically update Activity Manager with exposure assessment results. EHS works with the Activity Lead to document exposure assessment results in Activity Manager.
- Medical Surveillance — Activity Manager routes Medical Surveillance requirements for workers assigned to approved, active activities to CHESS. Completion or declination of medical surveillance is automatically reflected in Activity Manager as Additional Training on the Worker Summary page (see Section 4, Worker Summary Page of Work Process F, Assign and Authorize Workers).
- Co-located hazards: The Review Controls step in developing an activity includes a review of co-located hazards. Activity Manager displays Risk Level 3 and other hazards that are present during other activities in the same location that are not part of the activity under development.
- The Activity Lead may choose to customize existing controls and/or include additional controls (using the Add Additional Controls button) to mitigate potential risks from co-located hazards, e.g., fire mitigation measures due to the presence of flammable liquids.
- Divisions may choose to present division-specific controls for certain hazards, such as division-specific training found under “Qualifications” in the hazard matrix. Divisions work with their EHS liaison to incorporate division-specific controls into the Integrated Hazards Analysis.
Work Process E. Activity Manager: Release Activity for Review and Approval
- EHS Review and Concurrence (Level 3 only). Activities with Risk Level 3 hazards require EHS Division review.
- The Activity Lead initiates the EHS review process by selecting Initiate EHS Review from the Choose an Action drop-down menu.
- Once the Activity Lead releases an activity for EHS review, Activity Manager automatically routes the activity to the assigned EHS division liaison and the Risk Level 3 hazard SME(s). The DSC is also a collaborator in the Risk Level 3 activity review process.
- The division liaison sets the Collaboration Due Date in consultation with the Activity Lead and based on the Planned Start Date and activity’s complexity.
- The liaison and SME(s) review the scope of work, hazards, and controls, and request additional information from the Activity Lead as necessary. EHS may inspect the work locations and facilities supporting the activity and make recommendations based on such site visits.
- EHS collaborators have read/write access to the activity and assist the Activity Lead with customizing controls. Once the SMEs are satisfied with the hazards analysis, they indicate concurrence by selecting the “thumbs up” icon.
- The EHS liaison is responsible for providing final EHS Review Comments and releasing the activity to the Activity Lead to initiate line management approval. Additional changes by the Activity Lead after EHS has closed the collaboration will reset the activity to the Developing status.
- Collaborators receive My Work notifications as collaborators update the activity.
- Release for Line Management Approval and Approve Activity. The final step in the activity development process is line management approval:
- The Activity Lead initiates this process by selecting Release for Approval from the Choose an Action drop-down menu. This triggers a My Work Action notice and email to the next approver.
- The line management approval process depends upon the activity risk level and division settings.
|
|
Activity Risk Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Approver |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Activity Lead* |
Approve |
Approve |
Approve |
|
Project Lead |
Approve |
Approve |
Approve |
|
Division Safety Coordinator |
Notify |
Notify or Approve ** |
Approve |
|
Division Director (or designated approver) |
N/A |
N/A |
Approve |
|
*Automatic approval when the Activity Lead selects Release for Approval **Optional and routed based on division settings | |||
- THIS APPEARS AS 3 IN THE PUBLISHED PAGE. SHOULD APPEAR AS c. Approvers select Approve Activity or Reject Activity from the Choose an Action drop-down menu. Approved activities become Active, and workers assigned to the activity will receive notifications to Accept Conditions.
- THIS APPEARS AS 4 IN THE PUBLISHED PAGE. SHOULD APPEAR AS d. Rejecting an activity requires a reason and resets the activity to Developing status.
Work Process F. Activity Manager: Assign and Authorize Workers
- Assign Workers. The Activity Lead is responsible for assigning workers and authorizing them to perform work. This responsibility may also be delegated to one or more Activity Lead Designee(s) as described above. To assign and authorize workers:
- Navigate to the Assign Worker page by selecting the Workers icon.
- Enter the worker’s name or badge number in the Assign Workers field and click Add Worker and then click the SAVE button.
- Review worker’s training status to ensure all required training is complete. A red circle with a horizontal white line indicates one or more required trainings are not complete.
- Provide the necessary review of the activity and provide any necessary on-the-job training.
- Select the Authorization Level by clicking the Edit Info icon (pencil icon) and selecting from the available choices: Works Supervised, Works Unsupervised but Not Alone, or Works Alone. The default Authorization Level is Not Authorized to Work. Refer to Section 3, Authorize Worker, below for a description of authorization levels. Assign any task restrictions for individual workers. Click the check mark to save changes and close editing.
- The Activity Lead may assign a worker and set the authorization level while the activity is still under development. However, the worker receives notification of the assignment only after the activity is approved. Furthermore, the worker receives notification of assignment to work on a Risk Level 3 activity only after the worker’s supervisor approves of the worker’s participation on that activity.
- The icons to the right of the worker’s name indicates whether a worker has completed required activity-specific training, has been approved by their supervisor to participate on the activity, and has accepted the activity conditions. Click the Worker Info (“i”) icon to review the worker’s training details, waive training, or attach files such as OJT completion records.
- To remove a worker from an activity, the Activity Lead clicks the Delete (trash bin) icon.
- The Activity Lead is automatically added to the activity as Works Unsupervised but Not Alone pending the Activity Lead’s acceptance of the activity’s tasks, hazards, and controls. The Activity Lead will need to change their authorization level to Works Alone if appropriate.
- Waive Training. The Activity Lead may waive activity-specific training if the worker is not performing tasks within the activity that requires the course.
- Access the Assign Workers page by clicking the Workers icon.
- View the Worker Details for the applicable worker (“i” icon)
- Select “Not performing tasks” from the Waive training drop-down menu for the applicable training course(s).
- Confirm and click the SAVE button.
- Authorize Worker
- To authorize a staff member to perform an activity unsupervised, the Activity Lead must evaluate and provide the following:
- Berkeley Lab formal training — The Activity Lead compares the activity-required courses for each work activity against the employee’s training profile to verify that the staff member has completed all the required training classes, or waive the training if applicable as described above.
- On-the-Job training (OJT) — The Activity Lead must ensure the staff member receives the necessary OJT for the work activity. This OJT should include a review of the hazards and controls associated with the particular work activity.
- Worker proficiency — The Activity Lead must determine if the worker is proficient to perform the work activity safely and without supervision. To make this determination, the training must be completed and the Activity Lead must use their judgment based on interactions with, and work observations of, the worker.
- Workers are authorized at one of the following levels:
- Not authorized to work: default authorization level when worker is first added to an activity. The Activity Lead may assign a worker to an activity while the activity is under development or in review in order to determine the worker’s required training completion status.
- Work with Supervision: The Activity Lead may authorize a worker to work under supervision while the worker is in the process of completing required training, including on-the-job training.
- Work Unsupervised but Not Alone: By authorizing the worker to work unsupervised but not alone, the Activity Lead is certifying that the worker, through a combination of skills, experience and on-the-job training has the necessary competency to safely perform the work involved in the activity without direct supervision. Because of the hazards associated with the work, a second person must be present per the Berkeley Lab Working Alone Policy. Workers at Berkeley Lab are not allowed to work alone when the mitigated hazards associated with their work can incapacitate them such that they cannot self-rescue or activate emergency services.
- Work Alone: By authorizing the worker to work alone, the Activity Lead is certifying that the worker, through a combination of skills, experience, and on-the-job training has the necessary competency to safely perform the work involved in the activity without direct supervision. Furthermore, by authorizing Work Alone, the Activity Lead certifies that the activity does not include hazards that when mitigated could incapacitate the worker such that that they could not “self-rescue” or activate emergency services. Find the Working Alone Policy here.
- To authorize a staff member to perform an activity unsupervised, the Activity Lead must evaluate and provide the following:
- Worker Summary Page. The Worker Summary page provides a list of all activities to which the worker is assigned and the status of all activity-required training. The Worker Summary also presents the worker’s status on other select training courses, such as those that indicate completion of medical surveillance requirements.
- Supervisors can access the Worker Summary page by selecting the worker from the My Workers list, and clicking on View Worker Summary.
- Supervisors and Activity Leads can access the Worker Summary from within an activity per the following:
- Access the Assign Workers page by clicking the Workers icon.
- View the Worker Details for the applicable worker (“i” icon).
- Click on the worker’s name at the top of the Work Detail page.
- Supervisor Role. The worker’s supervisor may be someone other than the Activity Lead or Project Lead. In this instance, the worker’s supervisor is involved in the process on a risk-based approach.
- For Risk Level 1 and 2 activities, the supervisor receives a My Work notification informing them of the worker’s participation on the activity and no action is needed.
- For Risk Level 3 activities, the supervisor receives a My Work Action notification and an email, and must approve the worker’s participation before the workers can accept the conditions of the work. From the Worker Details page, select Approve Worker under Choose an Action. Supervisors can also approve multiple direct reports at the same time from the Assign Workers page.
Work Process G. Activity Manager: Review Activity and Accept Work Conditions
Review Activity Summary
- Activities in the Reviewing, Active, and Closed status appear in the Activity Summary view.
- The Activity Summary view presents the activity information in a tab format, one each for Description of Work, Hazards, and Controls.
- Clicking the icons at the top right of the page takes the user to the Workers list, Attachments, and History and Approvals.
- Choose an Action presents role-based options to print the activity and take other actions such as edit and close.
- Accept Work Conditions
- The worker is notified of the activity assignment via a My Work message and an email.
- Once the worker and Activity Lead review the tasks, hazards, and controls of the defined work, the worker selects Accept Conditions from the Choose an Action menu. If the worker believes he or she was mistakenly added to an activity, the worker should contact the Activity Lead or his/her supervisor to discuss the issue.
Work Process H. Activity Manager: Cancel Activity
The Activity Lead may cancel an activity in the Developing status.
- Canceling an activity permanently deletes the Developing activity from the Activity Manager system.
- To cancel an activity, select Cancel Activity from the Choose an Action menu and confirm.
Work Process I. Activity Manager: Close Activity
The Activity Lead may close an activity when work under the activity is no longer being performed:
- To close an activity, select Close Activity from the Choose an Action menu and confirm.
- The Activity Lead, workers, and workers’ supervisors (if not the Activity Lead or Project Lead) receive a My Work message informing them of the activity closure.
- Closed activities are accessible for viewing in the Activity Search menu.
Work Process J. Activity Manager: Edit Activity
Activity Leads should update activities to keep current activity location information, description of work, and hazards and controls. Activities in the Developing and Active statuses are available for editing.
- To edit a Developing activity, select the activity from the My Activities list. Activity Manager opens the activity and allows editing of all fields.
- To edit an Active activity, select Edit Activity from the Choose an Action menu:
- Activity Manager clones the Active activity and opens the cloned version as a new activity under development. The activity number does not change, and there is no change to the Active activity while the new version is under development.
- A red target symbol next to the activity number under My Activities indicates a new version of an existing activity is under development.
- To cancel the Edit Activity process, select Cancel Activity from the Choose an Action menu of a cloned activity under development.
- To accept the changes and complete the editing process, select Finish Edit Activity from the Choose an Action menu.
- Editing an active activity prompts approvals, notifications, and the requirement for workers to re-accept the activity conditions on a risk-based approach.
- Some edits force a renewal of the activity. See Work Process K, Activity Manager: Renew Activity.
Work Process K. Activity Manager: Renew Activity
Activities are renewed on a risk-based approach.
|
Risk Level |
Renewal Period |
|---|---|
|
1 – Low Hazard |
Every three years |
|
2 – Moderate Hazard |
Every two years |
|
3 – High Hazard |
Every year |
- Three conditions prompt an Activity Renewal:
- The standard renewal period is reached.
- The Activity Lead edits the activity, and the edit requires a new version.
- The Activity Lead chooses to renew an activity and extend the renewal period.
- Activity renewal requires the same level of EHS (Risk Level 3 only) and division line management review as creating a new activity.
- To Renew an Active Activity, select Renew Activity from the Choose an Action menu.
- Activity Manager clones the Active activity and opens the cloned version as a new activity under development. There is no change to the Active activity while the new version is under development.
- To cancel the Renew Activity process, select Cancel Activity from the Choose an Action menu of a cloned activity under development.
- To accept the changes and complete the Renewal process, select Initiate EHS Review (Risk Level 3 only) or Release for Approval from the Choose an Action menu. The activity number remains the same.
- At completion of the standard approval process, Activity Manager resets the Activity Renewal Date based on the risk-based renewal period (3 years for Risk Level 1; 2 years for Risk Level 2; and 1 year for Risk Level 3). Workers need to re-accept conditions when an activity is renewed.
Work Process L. Activity Manager: Delegate Role
Project Leads, DSCs, EHS liaisons, and supervisors may delegate their Activity Manager role to another person with system access. Activity Leads may not delegate their role; however, the Project Lead has privileges to take all actions on behalf of the Activity Lead or to designate a new Activity Lead. Activity Lead Designees may still add and authorize workers, and the DSC may take some actions on behalf of the Activity Lead.
- To delegate a role, select Delegate Role from the logged-in user’s menu.
- Enter the delegate’s name and specify delegation duration or select Open Ended.
- The My Delegations page also shows current delegations by others. System notifications and access are as follows:
- Activity Manager sends the delegator’s pending actionable My Work notifications to the Delegate. When a delegation expires or is canceled, Activity Manager removes the delegate’s privileges and all delegator’s actionable My Work notifications from the delegate’s My Work.
- The delegator’s (Project Lead) activities appear in the delegate’s My Activities list. The delegator’s activities are removed from the delegate’s My Activities when a delegation expires or is canceled.
- Either the delegator or the delegate has privileges to take action on open actionable items.
- A delegate may not delegate to another.
Work Process M. Delivery Options for Safety-Related Training
The Berkeley Lab Training system (BLT) is the system of record for all Berkeley Lab training. BLT receives safety-related training requirements in two ways:
- Activity Manager
- An Activity Lead defines an activity in Activity Manager and selects the associated hazards.
- Required and recommended training courses are presented as controls for the associated hazards.
- The Activity Lead assigns workers to the activity.
- Activity Manager sends activity training requirements for the assigned workers to the BLT.
- BLT sends training completion status information to Activity Manager. BLT also sends information about soon-to-expire and expired training classes.
- BLT Training Group
- A BLT training group owner works with EHS Training to create a training group.
- Staff are enrolled in the training group following one of these processes:
- Automatically (rule-based) depending on criteria such as organization code.
- Automatically (rule-based) depending on an attribute of the worker’s Activity Manager assignment. For example, activities performed in a particular location may require a location-based course. Activity Manager sends BLT information on workers authorized to work on activities occurring in the particular location, and the BLT sends the worker a training requirement notification.
- Automatically, via the Comprehensive Health, Environmental and Safety System (CHESS), based on medical surveillance requirements.
- Manually by the training group owner, for example, Train-the-Trainer for Crane Instructors.
Work Process N. Activity Manager: Assigning Opt-Out Status
All workers who are not performing Work must be opted out of the work planning & control process in Activity Manager. The Supervisor shall make the determination whether the worker is not performing Work. In those instances, the Supervisor opts the worker out of the work planning & control process.
- The Supervisor selects Workers/My Workers from the main menu; this produces a list of the workers who report directly to the Supervisor.
- For each worker to be opted out of the Activity Manager process, the Supervisor clicks on the “opt-out” box and then selects the appropriate criterion for the opt-out selection.
- A worker cannot be opted out if the worker has previously been assigned to an Activity. The worker will need to be removed from all Activities prior to being opted out.
There are three reasons to opt-out a worker:
• No Work Performed means the worker is not performing work at LBNL. An example would be a worker providing consultation or attending meetings, but not performing hands-on work at LBNL.
• UCB Campus Work Only means the person is working exclusively on the UC Berkeley campus (but not working in Donner Lab).
• Equivalent Authorization System means the worker is authorized by a different authorization system such as the Subcontractor Job Hazard Analysis, (SJHA), the Construction Job Hazard Analysis (cJHA), or the Advanced Light Source user group authorization process.
6.9 Source Requirements
- Code of Federal Regulations Title 29, Section 1910.119, Process Safety Management of Highly Hazardous Chemicals
- DOE O 420.2, Safety of Accelerator Facilities
- DOE O 435.1, Radioactive Waste Management (only those sections/subchapters adopted into the current LBNL Work Smart Standards set)
- California Code of Regulations Title 19, Section 2770.5, List of Substances
- California Code of Regulations Title 22, Section 6620.1 et seq., (California Hazardous Waste Regulations)
Other Driving Requirements
- United States Code Title 42, Section 4321 et seq. (NEPA, National Environmental Policy Act)
- California Public Resources Code, Section 2100 et seq. (CEQA, California Environmental Quality Act)
- 10 CFR 851.21, Hazard Identification and Assessment
- 10 CFR 851.22, Hazard Prevention and Abatement
6.10 Reference Documents
|
Document Number |
Title |
Type |
|---|---|---|
|
07.01.002.001 |
Chapter 1 General ES&H Requirements |
Program |
|
07.07.013.001 |
Chapter 4 Exposure Assessment |
Program |
|
07.02.003.001 |
Chapter 6 Work Planning and Control |
Program |
|
07.07.007.001 |
Chapter 10 Construction Safety |
Program |
|
07.08.001.001 |
Chapter 21 Radiation Safety |
Program |
|
07.04.001.001 |
Chapter 24 EHS Training Program |
Program |
|
07.02.04.001 |
Chapter 31 sJHA Process – Subcontractor Job Hazards Analysis |
Program |
|
PUB-3140 |
Program | |
|
03.02.002.001 |
Chapter 22 Research with Human and Animal Subjects |
Program |
6.11 Appendices
Appendix A. Work Planning and Control Equivalence Worksheet
Appendix B. Facility-Based Authorizations
Appendix C. Hazard-Specific Information Requirements
Appendix A. Work Planning and Control Equivalence Worksheet
The Berkeley Lab Work Planning and Control (WPC) program allows for the use of WPC systems that are functionally equivalent to the institutional systems provided by Berkeley Lab. This document provides an outline for demonstration of equivalence. Certification of equivalence is provided by the Environment/Health/Safety (EHS) Division Director.
- Provide the following:
- Name of the proposed equivalent WPC system
- “Owner” (responsible individual) of the system
- Population to whom the system applies (be specific — names are not required but a detailed description of what makes up this “group” is.)
- The Berkeley Lab WPC system to which equivalence is proposed
- Describe how the proposed system provides the following:
- Definition and analysis of the scope of work (in the level of detail prescribed in this program), the work tasks, the hazards associated with the tasks, and the controls necessary to mitigate the hazards
- Discussion between and concurrence of the worker and the supervisor/work lead on the analysis
- Specific time-limited authorization (signed by both worker and supervisor/work lead) to proceed with the analyzed work subject to the specified controls
- Periodic review of the WPC work authorization(s), updating the tasks, hazards, and controls if necessary, and reauthorization
- Coordination with Berkeley Lab’s institutional training data-management system to record training completion
- Retrieval capability for the WPC and associated work authorization (i.e., how can it be confirmed that a specific individual has completed an authorization form and is authorized to perform a piece of work?)
Submit this document and any desired supporting information to the EHS Division Director for review.
□ Approved _______________________________________________
EHS Division Director
Date:
Conditions of Approval:
Appendix B. Facility-Based Authorizations
- General
- Facility-based authorizations provide safety operating envelopes based on activities taking place within that facility. There are several formats of facility-based authorizations; examples are given in this Appendix. The Facilities Division prepares NEPA/CEQA documentation, and EHS prepares other facility-based authorizations, with technical input from the applicable operating divisions. The operating divisions within the affected facility are responsible for conducting work within the defined safety operating envelope specified by the authorization.
- As used here, a “facility” means any equipment, structure, system, process, or activity that fulfills a specific purpose. At Berkeley Lab, a “facility” of a facility-based authorization is generally a building, but in some cases may refer to an area within a building. Facility-based authorizations differ from line management authorizations and formal authorizations in the following ways:
- Line management and formal authorizations are based on individual activities, whereas a facility-based authorization is a function of an additional aggregate hazard, interaction between multiple operations, or a piece of facility equipment (for example, a paint spray booth or waste treatment facility).
- With the exception of authorizations for accelerators and initial safety analyses performed during the capital asset acquisition process, the operating division is generally not involved in obtaining or renewing facility-based authorizations; the activity is coordinated by Berkeley Lab (Facilities for NEPA/CEQA issues, EHS for all others). The divisions that operate accelerators or that will be the occupants of new buildings work intimately with EHS during preparation, review, and update of their respective facility-based authorizations.
- The need for facility-based authorizations may be triggered by new programs or facilities or by changes in existing programs or facilities. Once a facility-based authorization is in place, it must be reviewed periodically to ensure that actual operations comply with the operating envelope established for that facility.
- Work Planning: Determining If a Facility-Based Authorization Is Needed for New Programs and Facilities
- In general, the analysis to determine whether a facility-based authorization is necessary for a new program or facility is carried out during the program or facility proposal and planning process. The various mechanisms for review during the proposal and planning process are described in Berkeley Lab’s Integrated Environment, Health & Safety Management Plan.
- Facility-based authorizations may be required if the proposed work presents risks in excess of work already being performed at the facility or Berkeley Lab; if significant on-site or off-site adverse consequences might be expected if controls are not adequate to mitigate the risks; or if the work involves hazards not routinely encountered and accepted in the course of everyday living by the vast majority of the public. Safety analyses are also required as part of the DOE Capital Asset Acquisition Process and establish the baseline safety envelope for programs/projects taking place in newly acquired buildings at start-up.
- Certain conditions relating to the handling or storage of hazardous materials automatically require a facility-based authorization. In a manner similar to the formal authorization process (see above), the handling or storage of hazardous materials in quantities above trigger levels requires a facility-based authorization. Appropriate facility-based authorizations and applicable trigger levels are given in this appendix. This appendix does not list all applicable local, state, and federal requirements that might apply to operations within a facility, but it includes items that can affect planning and design decisions.
- Facility-Based Authorization Process. The authorization process varies depending on the facility-based authorization sought as documented in this appendix.
- Facility-Based Authorization Review/Reauthorization
- Facility-based authorizations with a built-in reauthorization schedule (for example, regulatory permits) are reviewed according to that schedule. Accelerator facility-based authorizations are reviewed per the procedures outlined in the Berkeley Lab Radiation Protection Group’s Procedure 703 (see also Chapter 21 Radiation Safety). Facility-based safety analyses prepared during the capital asset acquisition process are not reviewed after initial occupancy and operation of the building. Operations-based work authorization processes, including monthly building code compliance reviews by the Berkeley Lab Fire Marshal, evaluate the safety envelope resulting from program changes within the building.
- For facility-based authorizations for which an EHS department is responsible, including most regulatory permits, that EHS department coordinates the reauthorization according to its own internal procedures.
- Facility-Based Authorization Documentation. Documentation is specified for each authorization in the table below. Original facility-based authorizations, including amendments or changes as required, are generally retained by EHS.
| Hazard/Concern | Trigger Level | Formal Authorization Type | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
General on-site or off-site environment, health, or safety risks |
In excess of those already accounted for in Berkeley Lab’s NEPA and CEQA documentation |
| |
|
Acquisition is covered by DOE O 413.3A, Capital Asset Acquisition Process |
| ||
|
Air emission of pollutants into the environment |
Non-radioactive material |
| |
|
Radioactive material |
| ||
|
Asbestos removal/abatement |
>100 sq ft or >100 linear ft or >35 cu ft |
| |
|
Chemicals |
Discharges to the sanitary sewer system (sink, drain) in excess of permitted limits |
| |
|
Emissions/use in excess of listed quantities in Bay Area Air Quality Management District regulations |
| ||
|
Storage/use in excess of Threshold Quantities listed in the OSHA Process Safety Management regulation |
| ||
|
Storage/use in excess of planning quantities listed in the State of California Accidental Release Program (CalARP) (note: includes federal substances) |
| ||
|
Use/handling/emissions in excess of National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAPS) or Stationary Source limits |
| ||
|
Radiation or radioactive materials |
Accelerators: External radiation level thresholds listed in DOE O 420.2 |
| |
|
Discharges to the sanitary sewer system (sink, drain) in excess of permitted limits |
| ||
|
Storage/use in excess of Category 3 limits (Nuclear Facility Limits)2 |
| ||
|
Use/handling/emissions in excess of National Emission Standard for Hazardous Air Pollutants or Stationary Source limits |
| ||
|
Storm drain discharge |
Any discharge (including pollutants and sediments) to the storm drain system other than rainwater |
| |
|
Waste, generation or treatment of |
Hazardous or hazardous component of mixed |
Storage in excess of 90 days in a Waste Accumulation Area or storage of > 55 gal for > 1 year in a Satellite Accumulation Area |
|
|
Radioactive or radioactive component of mixed |
| ||
|
On-line treatment (e.g., acid neutralization) |
| ||
Appendix B Notes:
- The term “Hazard Analysis Report” was finalized under the 2006 revision of DOE O 413.3A and specifically applies to non-nuclear facilities (below Hazard Category 3 threshold as defined in 10 CFR 830, Subpart B). In previous versions of this order and the repealed DOE O 5481.1B, the term varied, and documents prepared at Berkeley Lab over the years have been named Safety Analysis Document or Operational Hazards Analysis Report. None of these documents are a Safety Analysis Document in the context of nuclear facilities (Berkeley Lab is not and does not have nuclear facilities), and functionally, they are the same as the Hazard Analysis Report per DOE O 413.3A.
- For any facility in which radionuclides will be stored or used, it must be specifically documented whether these limits (individually and the sum of fractions) will or will not be exceeded. The EHS Division and the applicable division will prepare this analysis, which is submitted to the Facilities Division to become part of the permanent planning record for that facility.
Appendix C. Hazard-Specific Information Requirements
Biological Hazards
The Description of Work (DOW) must include two additional items for certain activities with biological materials. The DOW must:
- State and identify the tasks that involve potential exposure to human materials that are considered blood-borne pathogen (BBP) materials and
- Assess the biological risks related to:
- Most Activity Manager (AM) Risk Level 3 biological hazards, including non-exempt recombinant research and use or storage of pathogens or Risk Group 2 or higher agents and
- Other biological hazards where risk is not clear through the AM hazards-selection process
The risk assessment noted above should identify and describe biological risks or concerns related to the specific biological agents or materials to be used or produced and/or the tasks to be performed. If hazards or concerns are minimal, explain. Examples of risks or concerns include worker exposure, recombinant risks, environmental risks, and regulatory requirements.
In addition:
- Explain risks or concerns (or the lack thereof) associated with non-exempt recombinant or synthetic biology experiments, including risks or concerns associated with the: a) hosts and vectors; b) DNA segments to be cloned; c) expression of genes; and d) resulting new or redesigned products, knowledge, or technology (e.g., cells, organisms, biological parts, biological devices, or biological systems).
- Also provide any additional description of how biosafety controls or means of containment used in this work mitigate the risks. Emphasis should be on operation-specific controls that mitigate risks for the materials or tasks of highest risk or concern.
EHS Biosafety Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) and/or the Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) review all activities with AM Risk Level 3 biological hazards. Sufficient risk-assessment information must be provided for SME and/or IBC concurrence or approval of the activity.
Radiological Hazards
The DOW should specifically note the handling of radioactive material and quantity used, or the operating techniques for radiation-generating devices (RGDs), throughout the experiment. Special safety concerns should also be included.
Where applicable, identify the maximum parameters available for the X-ray machine. Identify the following:
- Voltage (kVp)
- Current (mA)
- Exposure time (max)
- Anode material
- Window
- Filter(s) used
For RGDs, include a statement confirming that detailed operating procedures have been developed. The procedure must give detailed directions for the operation of the RGD.
_____________________