Contents
Approved by Jim Buehler
Revised 9/21
49.1 Policy
49.2 Scope
49.3 Applicability
49.4 Exceptions
49.5 Roles and Responsibilities
49.6 Definitions
49.7 Required Work Processes
49.8 Source Requirements
49.9 Reference Documents
Note:
🚩🚩 Denotes a new section
🚩 Denotes the beginning of changed text within a section
🛑 Denotes the end of changed text within a section
____________________
49.1 Policy
The Berkeley Lab Air Quality Program ensures that operations emitting hazardous or regulated air pollutants are identified and controlled. Permitted air-pollutant sources at Berkeley Lab include:
- Asbestos projects involving demolition or renovation where more than 100 square or linear feet of asbestos-containing material (ACM) is expected. These require a 10-day notification to the Bay Area Air Quality Management District (BAAQMD).
- Boilers (>2 MMBTU)
- Diesel generators (>50 hp)
- Off-road diesel vehicle use
- Fuel dispensing (unleaded gasoline and ethanol 85)
- Greenhouse gas (fugitive gas emissions)
- Large Spark Ignition (e.g., forklifts)
- Paint spray booth
- Refrigerant equipment (non-comfort-cooling refrigeration equipment containing more than 50 pounds of refrigerant)
- Sandblasting booth
- Soil vapor extraction systems
- Solvent used for wipe-cleaning activities
- Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6)
49.2 Scope
This program addresses stationary and mobile air-pollution sources at the Berkeley Lab.
Other off-site leased facilities are not covered, as the Berkeley Lab does not own the regulated equipment (e.g., boilers, emergency generators, or asbestos demo or renovation operations).
49.3 Applicability
Berkeley Lab employees, visitors, affiliates, and subcontractors who work with or operate equipment emitting air pollutants.
49.4 Exceptions
Because Berkeley Lab is a research and development institution, laboratories located in a Berkeley Lab building where the total laboratory floor space within the building is less than 25,000 square feet, or where the total number of fume hoods within the building is less than 50, provided that Responsible Laboratory Management Practices, as defined in BAAQMD Section 2-1-224, are used. Buildings connected by passageways and/or corridors shall be considered as separate buildings, provided that structural integrity could be maintained in the absence of the passageways and/or corridors and the buildings have their own separate and independently operating HVAC and fire suppression systems. For the purposes of this subsection, teaching laboratories that are exempt per BAAQMD Section 2-1-113.2.11 are not included in the floor space or fume hood totals. In addition, laboratory units for which the owner or operator of the source can demonstrate that toxic air contaminant emissions would not occur, except under accidental or upset conditions, are not included in the floor space or fume hood totals.
49.5 Roles and Responsibilities
| Role | Responsibilities |
|
Principal Investigators and Supervisors |
|
|
Employees |
|
|
Environmental Services Group (ESG) |
|
49.6 Definitions
| Term | Definition |
| Bay Area Air Quality Management District (BAAQMD) | The local agency responsible for regulating stationary sources of regulated or hazardous air pollutants in the San Francisco Bay Area |
| Emission | Any filtered or unfiltered substance released to the air from Berkeley Lab or from a Laboratory facility |
| Environmental surveillance | The collection and analysis of “use” records to determine compliance with applicable standards and permit requirements |
| Environmental occurrence | Any sudden or sustained deviation from a regulated or planned performance at an operation that has environmental protection and compliance significance |
| Hazardous air pollutant | Any pollutant listed in Section 112(b) of the Clean Air Act |
| Regulated air pollutants | Pollutants for which standards have been promulgated under the authority of the Clean Air Act, and which include the classes of substances defined as nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, toxic air contaminants, or ozone-depleting substances |
| United States Environmental Protection Agency | A federal agency responsible for enforcing environmental laws. In California, some of this responsibility is typically delegated to state and local regulatory agencies. |
49.7 Required Work Processes
Work Process A. General Requirements and Flowchart
Work Process B. Permits
Work Process A. General Requirements and Flowchart
Berkeley Lab operations that emit hazardous (nonradioactive) or regulated air pollutants are subject to the rules and regulations administered by the Bay Area Air Quality Management District (BAAQMD). Air emissions of radioactive materials are discussed in Chapter 11 Environmental Protection.
BAAQMD rules and regulations are designed to control emissions of particulates, inorganic gases, organic compounds, air toxics, and odors. They require any person who wishes to build, erect, alter, replace, operate, or use any article, machine, equipment, or other device that might cause the emission of air pollutants to first obtain a permit from the BAAQMD, unless it qualifies for one of the agency’s specific exemptions. Prior approval is also required for modifications to an already-permitted activity. The types of permitted air-pollution sources found at Berkeley Lab and their associated air pollutants are summarized in the table below:
Air Pollution Source(s) | Primary Pollutant(s) |
| Diesel-powered emergency standby generators and diesel vehicles | Diesel particulate matter |
| Epoxy mixing hood | Volatile organic compounds |
| Fuel dispensing | Gasoline and ethanol |
| Paint spray booth | Volatile organic compounds |
| Sandblast booth | Particulates |
| Soil vapor extraction operations | Volatile organic compounds |
| Solvent wipe cleaning | Volatile organic compounds |
| Asbestos removal | Asbestos dust |
| Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) use | Very potent greenhouse gas |
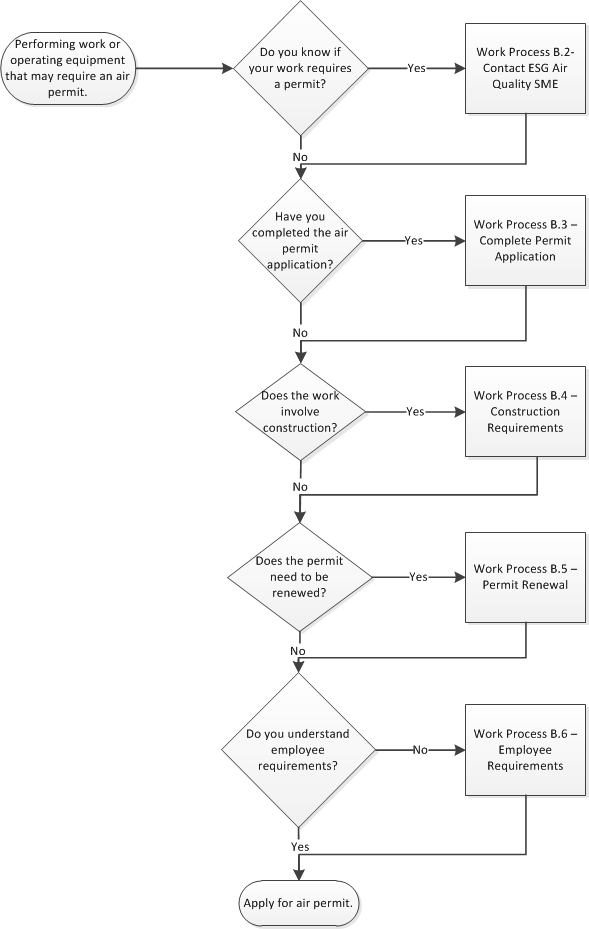
Work Process B. Permits
- The BAAQMD places operating conditions on each permitted air-pollution source. The agency is allowed specific lengths of time in its regulations to determine an application’s completeness and to evaluate and decide whether to approve the request. The process can be extended even further if the BAAQMD requests additional information at any stage, or if a risk assessment is required due to hazardous air pollutants emitted by the source. Because BAAQMD can take several months to complete this process, advance planning is essential in obtaining a new or modified permit in order to avoid operational delays.
- Contact Environmental Services Group Air Quality (Environmental/Nonradioactive) SME. The Environmental Services Group (ESG) provides technical assistance to each source owner/operator in meeting BAAQMD conditions. More information on the current set of air permits and associated operating conditions can be found on the ESG web site (link):
- Complete Permit Application. If it is determined that a permit is required, the ESG Air Quality SME prepares an application, with assistance from the owner of the activity. The application typically consists of a set of BAAQMD forms, a detailed description of the activity, diagrams, and maps.
- Construction Requirements. If an activity involves construction or installation of new equipment, an Authority to Construct is first issued by the BAAQMD. In most cases, construction and installation cannot begin until the Authority to Construct is received.
- Permit Renewal. When construction or installation has been satisfactorily completed and operations are ready to begin, the BAAQMD will issue a Permit to Operate. Permits are valid for one year, and require annual renewal.
- Each year, the BAAQMD will send permit-renewal forms to the ESG Air Quality SME to update information on permitted sources. Renewed permits are issued after the forms are returned and annual fees are paid.
- BAAQMD conducts periodic inspections of permitted sources. The inspection frequency depends on the risk posed by the source, and is determined by BAAQMD.
- Employee Requirements. Berkeley Lab employees are required to:
- Identify and notify ESG of unpermitted existing, new, and planned activities that emit materials to the air, either directly or through exhaust systems.
- Initiate purchasing or construction of air pollutant emitting equipment or processes only when authorized by the ESG Air Quality SME.
- Notify ESG of any upcoming equipment or process modifications, location changes, or changes in chemical usage that may affect permit status.
- Comply with permit conditions and operating standards.
- Submit related information to ESG in a timely manner for use in evaluating sources, preparing permit/exemption request applications, renewing permits, and responding to violation notices.
- Maintain complete and accurate records required by regulations and/or the Permit to Operate.
- Be available during both BAAQMD inspections, or DOE and ESG audits, and provide information requested by ESG personnel.
49.8 Source Requirements
- Bay Area Air Quality Management District (BAAQMD) Rules and Regulations Manual Implementing Documents
- BAAQMD Regulation 2: “Permits”
- BAAQMD Regulation 8, Rule 7: “Gasoline Dispensing Facilities”
- BAAQMD Regulation 8 Rule 16: “Solvent Cleaning Operations”
- BAAQMD Regulation 8, Rule 47: “Air Stripping and Soil Vapor Extraction Operations”
- BAAQMD Regulation 8 Rule 51: “Adhesive and Sealant Products”
- BAAQMD Regulation 9, Rule 7: “Nitrogen Oxides And Carbon Monoxide from Industrial, Institutional, and Commercial Boilers, Steam Generators, And Process Heaters”
- BAAQMD Regulation 11, Rule 2 “Asbestos Demolition and Renovation and Manufacturing”
- BAAQMD Regulation 12, Rule 4: “Sandblasting”
- 17 CCR 93115 ATCM for Stationary Diesel Engine
- 17 CCR 95340 to 95346 CARB Regulation for Reducing Sulfur Hexafluoride Emissions
- 17 CCR Division 3, Chapter 1, Subchapter 10, Article 4, Regulations to Achieve Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions
Other Driving Requirements
- 13 CCR article 4.8, chapter 9, sections 2449, 2449.1, 2449.2, and 2449.3
- 13 CCR sections 2430–24383
- California Air Resources Board (CARB) Off-Road Large Spark-Ignition Engines
- California Code of Regulations (CCR), AB 1085 CARB Refrigerant Management Program
- CARB Truck and Bus Regulation (Heavy Duty Vehicles)
- CARB Test-site designation for Ethanol 85 dispensing
- CARB Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) Reduction from Non-Electric and Non-Semiconductor Applications
- CARB Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) Emission Reductions from Gas Insulated Switchgear
49.9 Reference Documents
| Document number | Title | Type |
| 07.09.001.002 | Asbestos Hazards and Controls | Program |
_______________________