Contents
Approved by Karla Arredondo
Revised 8/25
41.1 Policy
41.2 Scope
41.3 Applicability
41.4 Exceptions
41.5 Roles and Responsibilities
41.6 Definitions
41.7 Required Work Processes
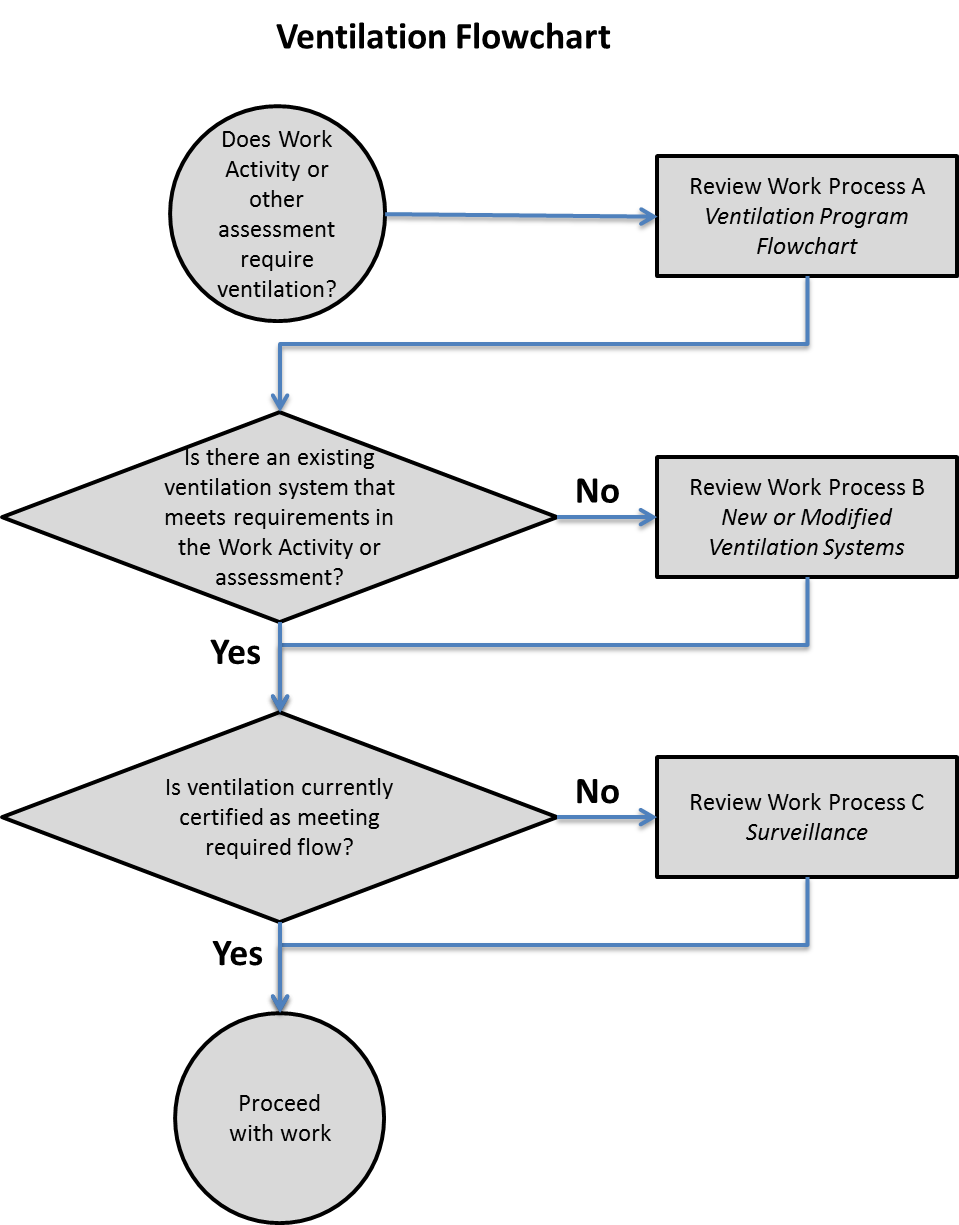
- Work Process A. Ventilation Program Flowchart
- Work Process B. New or Modified Ventilation Systems
- Work Process C. Surveillance
41.8 Source Requirements
41.9 Reference Documents
Note:
🚩🚩 Denotes a new section
🚩 Denotes the beginning of changed text within a section
🛑 Denotes the end of changed text within a section
___________________
41.1 Policy
The Berkeley Lab Ventilation Program protects workers and the environment by reducing airborne concentrations of contaminants through the following work-process requirements:
- The Environment, Health, and Safety Division (EHS) must be consulted to determine applicable design, construction, and performance standards for new ventilation systems used for contamination control, and must be notified of the purchase of hoods, glove boxes, filtering equipment, emissions-collection equipment, and other relevant ventilation items. (See Work Process B).
- New and relocated ventilation systems may not be used for contamination control until installation and performance have been evaluated and labeled by EHS and verified to meet application standards (See Work Process B).
- Line management must ensure that ventilation systems that do not meet performance standards (i.e., are deficient) are repaired, and are used within safety limits (if allowed) until repaired (See Work Process C).
- Performance of ventilation systems, including HEPA-filtered units, must be periodically evaluated (See Work Process C).
41.2 Scope
The Ventilation Program includes:
- Laboratory fume hoods
- Inert atmosphere glove boxes
- Negative-pressure glove boxes
- HEPA-filtered vacuum cleaners
- In-place HEPA filters used for contaminant control
- Biological safety cabinets (which include HEPA filters)
- Gas cabinets
- Laminar flow fume hoods
- Laminar flow cabinets (e.g. clean benches), and
- Other local exhaust ventilation systems, such as extractor arms, exhausted enclosures, ventilated tanks, back-draft benches, canopy hoods, etc.
41.3 Applicability
Berkeley Lab employees, casual and participating visitors, affiliates, and subcontractors who work with hazardous substances
41.4 Exceptions
None
41.5 Roles and Responsibilities
|
Role |
Responsibilities |
|
Facilities Division |
|
|
EHS Division, Health and Safety Department |
|
|
Line Managers |
|
|
Supervisors and Work Leads |
|
|
Ventilation System Users |
|
41.6 Definition
| Term | Definitions |
| HEPA filters | High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, used to filter hazardous chemical, biological, or radioactive particles. A HEPA filter has a minimum efficiency of 99.97% when challenged with an aerosol containing 0.3 micron particles. |
| Fume hood | A box-like structure with a sash or sashes that move vertically and/or horizontally across the front opening. Fume hoods are designed to contain and exhaust airborne contaminants generated inside its enclosure. |
41.7 Required Work Processes
Work Process A. Ventilation Program Flowchart
Work Process B. New or Modified Ventilation Systems
Work Process C. Surveillance
Work Process A. Ventilation Program Flowchart
Work Process B. New or Modified Ventilation Systems
- The Environment, Health, and Safety Division (EHS) must be consulted to determine applicable design, construction, and performance standards for new ventilation systems used for contamination control. EHS must be notified of the purchase of hoods, glove boxes, filtering equipment, emissions-collection equipment, and other relevant ventilation items. EHS may review the use of such ventilation systems with the requestor.
- New systems for contaminant control — including local exhaust ventilation systems, hoods, and in-place filters — must meet the requirements of applicable codes including California Building Code, the California Mechanical Code, and the California Fire Code. In addition, applicable industry standards must be consulted for guidance. These standards include those promulgated by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists; the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers; the American Industrial Hygiene Association; and the American National Standards Institute. EHS must be consulted to determine the applicable design, construction, and performance standards applicable to a project.
- Responsibility for assuring code compliance and conformance with applicable standards and requirements rests as follows:
- For projects executed by the Facilities Division, the Project Manager is responsible.
- For projects not executed by Facilities, the activity line manager responsible for the activity is responsible.
- New or relocated fume hoods and gas cabinets must be provided with electronic flow meters to indicate the velocity of air flowing into the hood, and to sound an alarm when the velocity falls outside permissible range. Other new or relocated exhaust systems used for contaminant control must have a visible means of indicating that the system is operating properly, such as a pressure gauge or manometer. These indicators are in addition to any monitoring devices installed as part of building operations.
- New fume hood systems, including those involving fume hoods relocated from another location, must be tested in accordance with applicable tests contained in ASHRAE 110-2016 as a condition of acceptance. The tracer gas containment test must conform to the 4.0 AI 0.1 criteria contained therein. This testing is performed by a third party, is paid for by the project, and must be validated (generally by witnessing) by EHS.
- New systems may not be used for contaminant control until their installation and performance have been evaluated and verified to meet applicable standards established by EHS, and they have been labeled as such.
Work Process C. Surveillance
- Surveys
- EHS must conduct periodic surveys of the performance of contaminant-control systems on the following schedule:
- The following types of laboratory fume hoods are surveyed on a one-year rotation:
- Radiological fume hoods
- Perchloric acid fume hoods
- Laminar flow fume hoods.
- All other types of fume hoods are surveyed on a two-year rotation.
- For those years when a survey is not due on a fume hood, an assurance check is completed. An assurance check is an abbreviated survey intended to confirm adequate performance of a hood using fewer sampling points. The result is then compared to the digital monitor/controller, if present. If the hood performance fails or is inadequate, or if the monitor/controller is found to be out of calibration, then a survey is performed. The survey frequency is then reset to the two-year rotation, with the assurance check during the intervening year.
- A smoke test will be performed annually during the two-year rotation or assurance check.
- Biological safety cabinets used for personnel protection are certified by an external vendor on a nominal one-year rotation. EHS verifies that the certifications have been performed by checking that the certification sticker is current.
- Vacuum cleaners equipped with HEPA filters and used for personnel protection are tested on a nominal one-year rotation.
- Other contaminant-control ventilation systems, including those with in-place filters, are surveyed for proper operation on a nominal one-year rotation.
- Nonspecific systems such as general laboratory or shop exhaust, equipment (e.g., vacuum pump) exhaust, mechanical room exhaust, and the like are monitored by the Facilities Division — often through the Facilities Management and Control System (FMCS) — and are not surveyed by EHS.
- The following types of laboratory fume hoods are surveyed on a one-year rotation:
- Surveys are scheduled so that all hoods in a given building are due on the last day of a particular month, and are past due three months after that date.
- Some HEPA filter-equipped systems are used for product protection only (e.g., as “clean benches” for maintaining sterility of non-infectious organisms; for clean assembly of optical or vacuum systems; as supply HEPA filters in semiconductor or nanomaterials fabrication rooms). EHS can assist in setting up testing of these systems, but the responsibility and expense for the testing belong to the research program.
- EHS must conduct periodic surveys of the performance of contaminant-control systems on the following schedule:
- Hoods and Local Exhaust Points
- EHS establishes minimum standards of performance for each hood or system based on code requirements, nationally recognized standards, and good professional judgment. The performance standard for each hood is listed in the computerized record for that hood. If a hood fails to meet the minimum performance standard, it is considered deficient.
- Line management must ensure that ventilation systems that do not meet performance standards (i.e., are deficient) are repaired. Until repairs are completed, line management must also ensure that deficient systems are not used (if tagged “out of service”) or are used within safety limits (if allowed and tagged as such).
- Recordkeeping Requirements
- The results of all calibration, certification, and other surveys are recorded in the Berkeley Lab’s Ventilation Database and maintained by the EHS Division. The database is considered the point of record.
- A hard copy of each survey and assurance check is also filed and maintained by the EHS Division.
- All systems that are monitored by EHS have stickers that indicate when the last survey or assurance check was performed.
- Additional Information
- For questions about the database, or to have the performance of local exhaust systems evaluated, contact the EHS Ventilation Program Coordinator.
- For information regarding the testing of HEPA vacuums and HEPA filtering systems, contact the EHS HEPA Filter Program Coordinator.
41.8 Source Requirements
In addition to this document, the following regulations contain applicable information:
- 10 CFR 851, Worker Safety and Health Program
- California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Subchapter 7. General Industry Safety Orders,
- Group 16. Control of Hazardous Substances,
- Article 107. Dusts, Fumes, Mists, Vapors and Gases (Sections 5143, 5150.-5154.2):
- 5143 General requirements of Mechanical Ventilation Systems.
- 5150. Ventilation and Personal Protective Equipment Requirements for Welding, Brazing and Cutting.
- 5151. Ventilation and Personal Protective Equipment Requirements for Abrasive Blasting Operations.
- 5152. Ventilation and Personal Protective Equipment Requirements for Grinding, Polishing, and Buffing Operations.
- 5153. Ventilation and Personal Protective Equipment Requirements for Spray Coating Operations.
- 5154. Ventilation and Personal Protective Equipment Requirements for Open-Surface Tank Operations.
- 5154.1. Ventilation Requirements for Laboratory-Type Hood Operations.
- 5154.2. Ventilation Requirements for Biological Safety Cabinets.
- Article 109. Hazardous Substances and Processes
- 5191. Occupational Exposure to Hazardous Chemicals in Laboratories.
- Article 107. Dusts, Fumes, Mists, Vapors and Gases (Sections 5143, 5150.-5154.2):
- Group 20. Flammable Liquids, Gases, and Vapors,
- Article 135. General (Sections 5416 – 5420):
- 5416. Flammable Vapors.
- 5417. Flammable Liquids–General.
- 5418. Carboys and Drums Containing Flammable Liquids.
- 5420. Tanks, Vats and Containers Containing Flammable Liquids.
- Article 137. Spray Coating Operations
- 5446. Spray Booths
- Article 135. General (Sections 5416 – 5420):
- Group 16. Control of Hazardous Substances,
- DOE P 450.4A, Integrated Safety Management System Policy
- DOE M 450.4-1, Integrated Safety Management System Manual
- NFPA 45 Section 7.14, Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance
- U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, Modification No. 400, Section H.30, Contractor Assurance System
41.9 Reference Documents
| Document Number | Other Reference | Title | Type |
| N/A | ACGIH Ventilation Manual, relevant sections | Consensus standard | |
| N/A | PUB-5341 | Chemical Hygiene and Safety Plan, Hazard Controls section | Procedure |
| N/A | PUB-3435E | Biosafety Manual, Section 5.6.4, Ventilation and Hoods | Procedure |
| N/A | PUB-3140 | Integrated Environment, Safety & Health Management Plan | Procedure |
| N/A | ES&H Manual Chapter 4, Section 4.15 | Procurement | Procedure |
| 12.01.002.000 | Procurement of Goods and Services | Policy | |
| In-Place HEPA Filter Leak Testing Procedure | Procedure | ||
| Restricted Items List | Form |
_____________________