Contents
Approved by Brendan Mulholland
Revised 09/21
55.1 Policy
55.2 Scope
55.3 Applicability
55.4 Exceptions
55.5 Roles and Responsibilities
55.6 Definitions
55.7 Required Work Processes
55.8 Source Requirements
55.9 Reference Documents
Note:
🚩🚩 Denotes a new section
🚩 Denotes the beginning of changed text within a section
🛑 Denotes the end of changed text within a section
___________________
55.1 Policy
The Sanitary Sewer Program ensures that Berkeley Lab remains in compliance with sewer discharge limits imposed by the East Bay Municipal Utility District (EBMUD) by:
- Assisting dischargers by reviewing their potential discharge to see if it is eligible for sanitary-sewer disposal;
- Maintaining sitewide, treatment unit, and other special discharge permits with EBMUD;
- Submitting periodic self-monitoring reports to EBMUD as required by each EBMUD permit;
55.2 Scope
This Sanitary Sewer Program covers discharges to the sanitary sewer from the Berkeley Lab main site.
55.3 Applicability
All Berkeley Lab employees, visitors, affiliates, and subcontractors who intend to discharge hazardous substances into the sanitary sewer.
55.4 Exceptions
None
55.5 Roles and Responsibilities
|
Role |
Responsibilities |
|
East Bay Municipal Utility District (EBMUD) – the local wastewater treatment facility |
Accepts and regulates sanitary-sewer discharges from Berkeley Lab |
|
Employees |
|
|
Environmental Services Group (ESG) |
|
|
Principal investigators and supervisors |
|
|
State Water Resources Control Board (SWRCB) |
Regulates sanitary-sewer discharges to San Francisco Bay from Publicly Owned Treatment Works (POTW) |
|
Waste Management Group |
|
55.6 Definitions
| Term | Definition |
| Effluent | Any treated or untreated liquid discharge from a Berkeley Lab site or facility |
| Environmental monitoring | The collection and analysis of sanitary-sewer samples |
| Environmental occurrence | Any sudden or sustained deviation from a regulated or planned performance at an operation that has environmental protection and compliance significance. Specifically, a violation of a water-district permit or ordinance requirement. |
| Hazardous wastes | Wastes exhibiting any of the following characteristics: ignitability, corrosivity, reactivity, and toxicity. In addition, EPA has listed specific wastes as hazardous that do not necessarily exhibit these characteristics. |
| Publicly Owned Treatment Works (POTW) | A sewage-treatment plant. The East Bay Municipal Utility District plant is the POTW that accepts sewage from Berkeley Lab. The Central Contra Costa Sanitary District plant is the POTW that accepts sewage from JGI. |
| Radionuclide | A natural or artificially produced isotope that spontaneously undergoes radioactive decay |
55.7 Required Work Processes
Work Process A. General Requirements
- Discharge Permits
- Discharges to the sanitary-sewer system are subject to increasingly complex and restrictive standards imposed by EBMUD at the Berkeley Lab main site.
- EBMUD has established a permitting process that mandates operating conditions that must be met for all wastewater discharged into their sanitary-sewer system.
- At the Berkeley Lab main site, EBMUD has established three wastewater discharge permits for:
- Sitewide activities
- Wastewater pretreatment units at the Building 77 Ultrahigh Vacuum Cleaning Facility
- Groundwater treatment systems at various locations
- EBMUD Special Discharge Permits are required for the discharge of stormwater from construction sites or the discharge of groundwater to the sanitary sewer (e.g., Old Town Demolition Project, Bayview / SURP / BioEPIC Project).
- Berkeley Lab Discharge Limits. These wastewater discharge permits specify different discharge limits at the site boundary and at the treatment units. Table 1 shows the substances for which Berkeley Lab has EBMUD-specific discharge limits.
Table 1. EBMUD Sanitary Sewer Discharge Limit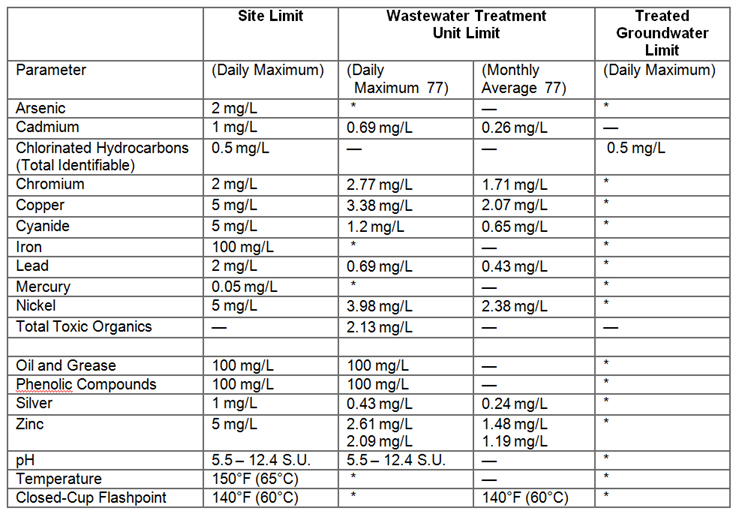
* See sitewide discharge limits
- Terms of the wastewater discharge permits require that Berkeley Lab abide by all applicable provisions of the EBMUD ordinance and any other federal, state, and local regulations.
- California regulations governing standards for the protection against radiation are found in 17 CCR 30253. Limits for radionuclide discharges are found in 10 CFR 20.2003.
- Because of EBMUD discharge limits, no discharge may be made to the sanitary-sewer system until the composition and concentration of the discharge is known. The Generator Assistant within the Waste Management Group will assist in determining if the waste to be disposed of is a hazardous waste.
- In some cases, sampling and analysis must be performed to determine if a discharge can be released to the sewer. ESG will assist employees in determining whether their discharge is eligible for sanitary-sewer disposal.
- Approval for release to the sewer can be issued only after all required analyses have been conducted and properly evaluated.
- In addition, ESG performs periodic wastewater discharge sampling and reports the results to EBMUD, as mandated by each permit.
- All sinks should be labeled to warn against disposal of hazardous substances down the drain.
55.8 Source Requirements
- 10 CFR 20.2003, Disposal by Release into Sanitary Sewerage
- EBMUD Ordinance No. 311A.03 (except AEA discharges)
Other Driving Requirements
- EBMUD permit #6600791(main site), #50238911 (B77 FTU), #50347891 (Groundwater Treatment Systems),
55.9 Reference Documents
None
_____________________